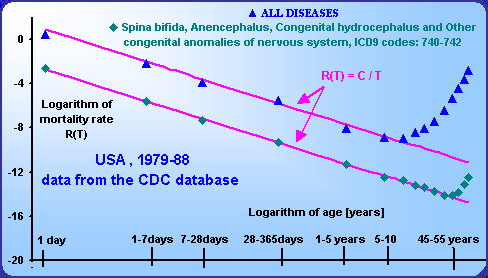
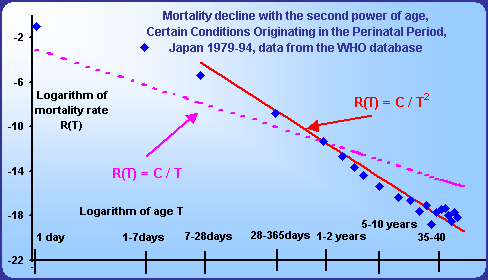
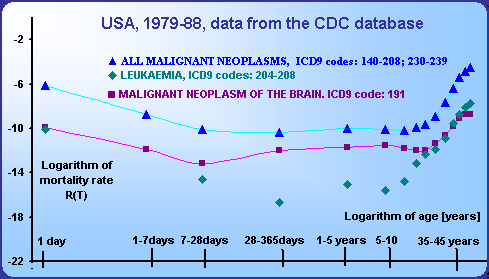
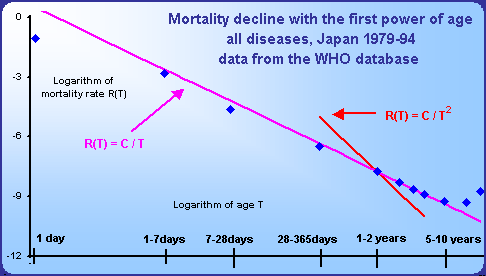
 Postnatal mortality declines with the first or with the second power of age.
This decline continues minimally till the age of 10. Mortality rate declines for all particular diseases except malignant neoplasms minimally from the first year of life.
The regression straight lines within the log-log scale are practically identical with the straight lines with the slope -1 or -2 drawn through the point of the age category 1-2 years.
Postnatal mortality declines with the first or with the second power of age.
This decline continues minimally till the age of 10. Mortality rate declines for all particular diseases except malignant neoplasms minimally from the first year of life.
The regression straight lines within the log-log scale are practically identical with the straight lines with the slope -1 or -2 drawn through the point of the age category 1-2 years.